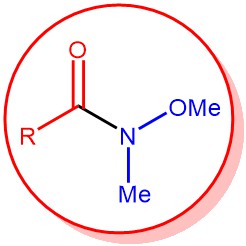
The synthesis of ketones from N-methoxy-N-methyl amide, called as Weinreb amide, using organometallic reagents is known as the Weinreb ketone synthesis. Generally, the direct conversion of acid chlorides or esters to ketones using organometallic reagents does not result in a high yield of ketones because the intermediate ketones are highly reactive towards the organometallic reagents and over-addition results in the formation of tertiary alcohol as the major product.
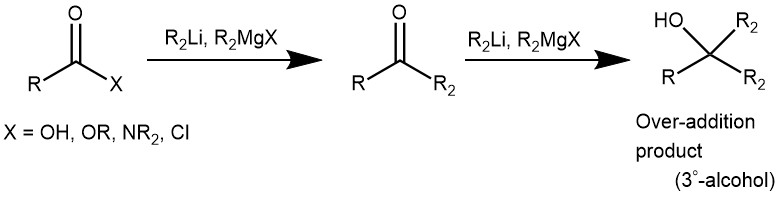
Thus in 1981, S. M. Weinreb and S. Nahm discovered that the addition of excess Grignard reagent or organolithium species to N-methoxy-N-methyl amides (Weinreb amide) resulted in the formation of ketones upon the acidic workup. Hence, stepwise conversion of carboxylic acid and its derivatives (ester, acid chloride, anhydride) to the corresponding Weinreb amide and subsequent treatment of this species with an organometallic reagent (like Grignard reagent, organolithium) to form a ketone is called as Weinreb Ketone synthesis.

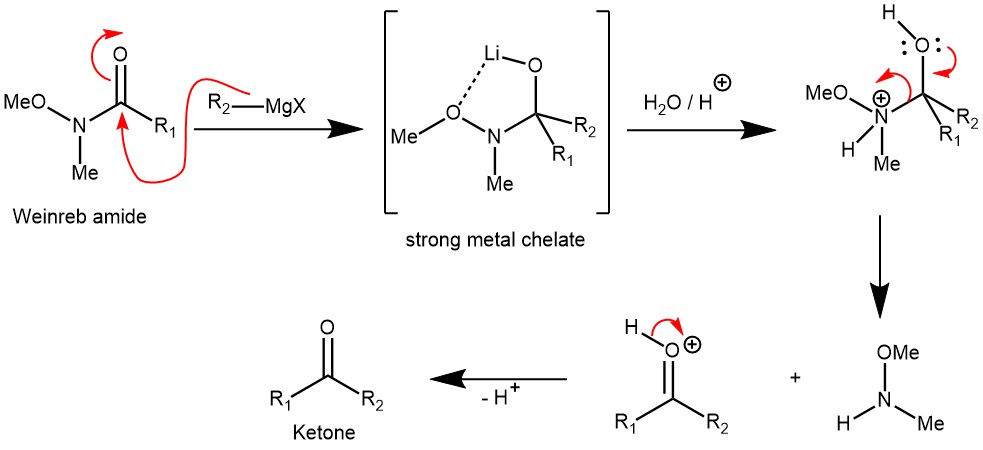
MECHANISM: Synthesis of ketone from Weinreb amide using organometallic reagents. For the synthesis of Weinreb amide check the link.
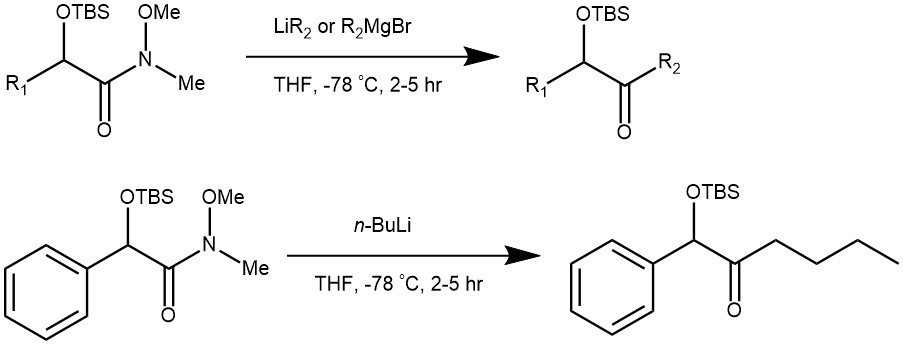
EXAMPLE 1: The α-siloxy Weinreb amide (186 mg, 0.60 mmol, 1.0 mol equiv) was dissolved in dry tetrahydrofuran (0.12 M) and cooled to –78 °C in a dry ice/acetone bath under argon. The organometallic reagent n-butyllithium (1.34 M solution in hexanes, 493 μL, 0.66 mmol, 1.1 mol equiv) was added dropwise and the resulting solution was stirred at –78 °C for 2.5 hours. The reaction was quenched with saturated aqueous NH4Cl and extracted three times with ethyl acetate. The combined organic layers were dried over Na2SO4, filtered, and concentrated under reduced pressure. Purification via Flash column chromatography (SiO2; 5% EtOAc in PS 40–60 °C) afforded α-siloxy ketone 21 as a colourless oil (153 mg, 83%).[REF: J. Org. Chem. 2022, 87, 9408−9413]
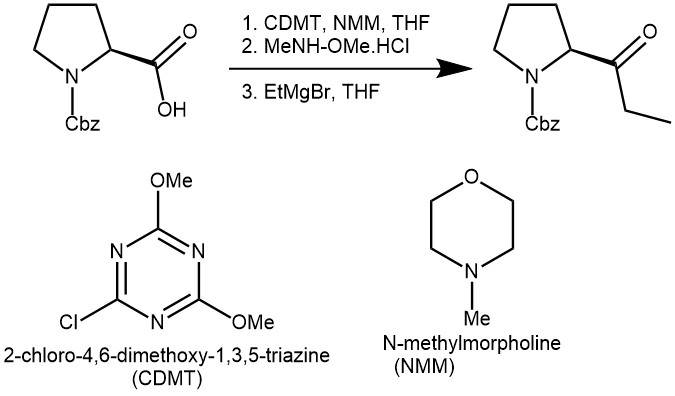
EXAMPLE 2: To a solution of N-benzyloxycarbonyl-L-proline (0.89 g, 3.7 mmol) in THF (11 mL), at room temperature, were added CDMT (0.74 g, 4.4 mmol) and NMM (1.2 mL, 11.1 mmol). A white precipitate was formed during stirring for 1 h, and then N,O-dimethylhy-droxylamine hydrochloride (0.36 g, 3.7 mmol) was added. The mixture was stirred for additional 8 h and then the solid filtered off under argon. The solution was added at room temperature to a THF solution (11 mL) of ethylmagnesium bromide (2.46 mL of 3 N in Et 2O, 2.5 mmol), stirred for additional 0.5 h, and then quenched with aqueous saturated NH4Cl and extracted two times with 10 mL of diethyl ether. The combined organic phases were washed with 15 mL of a saturated solution of Na 2CO3, followed by 15 mL of a solution 1 N HCl and brine. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous Na2SO4 to give, after evaporation of solvent, crude N-benzyloxycarbonyl-pyrrolidin-2-yl-propan-1-one (85%), that was further purified by flash-chromatography(EtOAc-hexane ) 6:4) (67%). [REF: J. Org. Chem., Vol. 66, No. 7, 2001]
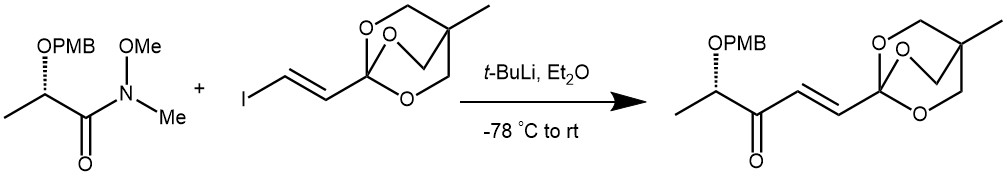
EXAMPLE 3: To a solution of t-BuLi (1.5 M solution in pentane, 3.8 mL, 5.7 mmol) in Et 2 O (10 mL) at – 78 °C was added a solution of the iodovinyl OBO ortho ester 6 (810 mg, 2.9 mmol) in Et 2 O (10 mL). After the mixture was stirred for 5 h at – 40 o C, a solution of the Weinreb amide 8 (170 mg, 0.70 mmol) in Et 2 O (10 mL) was added at – 78 °C. The reaction mixture was warmed to the room temperature and stirred for 12 h and quenched with H2 O. The reaction mixture was extracted with EtOAc and the combined organic layers were washed with brine, dried over Na 2SO4 and concentrated in vacuo. The residue was purified by flash column chromatography on silica gel (EtOAc : n-hexane : Et 3 N = 25 : 75 : 2) to afford 220 mg (90%) of ketone 9 as a colorless oil.[REF: Org. Lett., Vol. 7, No. 15, 2005, 3159-3162]
REFERENCES:
- Strategic applications of named reactions in organic synthesis by Laszlo Kurti and Barbara Czako
- Chem. Commun., 2012,48, 9610-9612
- Weinreb ketone synthesis. (2023, July 22). In Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Weinreb_ketone_synthesis
- https://mychemblog.com/weinreb-amide-synthesis-part-i-weinreb-amide-preparation/