PROTECTION OF AMINE: di-tert-butyl dicarbonate [Boc anhydride (Boc)2O]: Boc protection
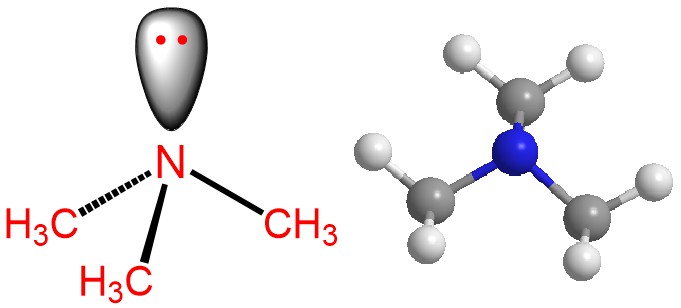
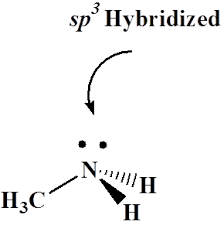
Amines are reactive functional groups that can participate in a variety of chemical reactions. While this reactivity can be advantageous in some reactions, it can also be problematic in others. For example, amines can react with other reagents or functional groups in the reaction mixture, leading to unwanted side reactions or products. To prevent these …
PROTECTION OF AMINE: di-tert-butyl dicarbonate [Boc anhydride (Boc)2O]: Boc protection Read More »